Contents in this Article
- AP TET Syllabus PDF- APTET URDU Paper 1 & Paper 2 Syllabus – PDF & Exam Pattern
- AP TET URDU Teacher Syllabus 2024
- Download AP TET Urdu Teacher Paper I Syllabus 2024
- 2. UNDERSTANDING LEARNING
- 3. PEDAGOGICAL CONCERNS
- II LANGUAGE (Urdu)
- PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- IV. MATHEMATICS (Marks: 30)
- PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- AP TET Urdu Paper 2 Syllabus 2024 PDF
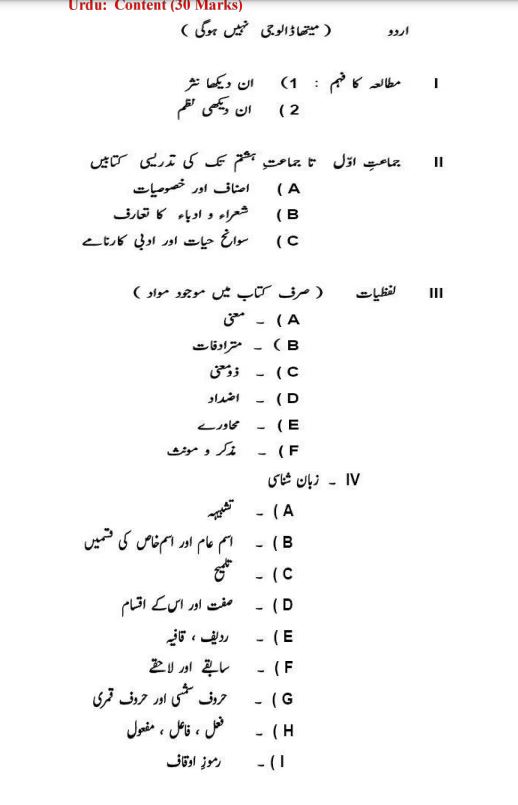
- 2. LANGUAGE – I Urdu (Marks: 30)
- IVa. MATHEMATICS & SCIENCE (Marks: 60) MATHEMATICS – CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- IV(a). SCIENCE – CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- IVb. SOCIAL STUDIES (Marks: 60) CONTENT (Marks: 48)
AP TET Syllabus PDF- APTET URDU Paper 1 & Paper 2 Syllabus – PDF & Exam Pattern
AP TET Syllabus 2024 in Telugu PDF Subject Wise. Andhra Pradesh TET Urdu Syllabus and Exam Pattern are available now. Here We Provide APTET Urdu Paper I & Paper II Syllabus. Candidates who applied for the Andhra Pradesh AP TET Jobs have started their Exam preparation for the Written Test which is going to organize by the Andhra Pradesh State Teacher Eligibility Test (AP TET). All those applicants AP can check the AP TET Syllabus and can download it. Here we also provided the AP TET syllabus 2024. So before going to begin the preparation, once check the Provided TET Syllabus 2024. Candidates can also get AP TET Syllabus 2024 in Telugu PDF from here for free of cost.
AP TET URDU Teacher Syllabus 2024
| Organization Name | Commissioner of School Education Andhra Pradesh Teacher Recruitment Board |
| Test Name | Andhra Pradesh Teacher Eligibility Test (AP TET) |
| Category | URDU Teacher Syllabus |
| Selection Process | Written Test |
| Location | Andhra Pradesh |
| Official Site | aptet.apcfss.in |
Download AP TET Urdu Teacher Paper I Syllabus 2024
PAPER I – SYLLABUS
CHILD DEVELOPMENT AND PEDAGOGY (Marks: 30)
- DEVELOPMENT OF CHILD
- Development, Growth & Maturation – Concept & Nature
- Principles of Development & their educational implications
- Factors influencing Development – Biological, Psychological, Sociological
- Dimensions of Development and their interrelationships – Physical & Motor, Cognitive, Emotional, Social, Moral, Language relating to Infancy, Early Childhood, late Childhood,
- Understanding Development – Piaget, Kohlberg, Chomsky, Carl Rogers, and Erikson
- Individual differences – Intra & Inter-Individual differences in the areas of Attitudes, Aptitude, Interest, HabiAP, Thinking (Divergent & Convergent), Intelligence and their Assessment
- Development of Personality – Concept, Factors affecting the development of Personality, Child Rearing Practices, Self-Concept
- Adjustment, Behavioral problems, Defense Mechanisms, Mental Health
- Methods and Approaches of Child Development – Introspection, Observation, Interview, Case study, Experimental, Rating Scales, Anecdotal Records, Questionnaire, Cross-sectional and Longitudinal
- Developmental tasks and Hazards
2. UNDERSTANDING LEARNING
- The concept, Nature of Learning – Input – Process – Outcome
- Factors of Learning – Personal and Environmental
- Approaches to Learning and their applicability – Behaviorism (Skinner, Pavlov, Thorndike), Constructivism (Piaget, Vygotsky), Gestalt (Kohler, Koffka) and Observational (Bandura)
- Dimensions of Learning – Cognitive, Affective and Performance
- Motivation and Sustenance -iAP role in
- Memory & Forgetting
- Transfer of Learning
3. PEDAGOGICAL CONCERNS
- Teaching and iAP relationship with learning and learner
- Learners in ContexAP: Situating learner in the socio-political and cultural context
- Children from diverse contexts – Children With Special Needs (CWSN), Inclusive Education
- Understanding of Pedagogic methods – Enquiry based learning, Project based learning, Survey, Observation, and Activity-based learning, Co-operative & Collaborative learning
- Individual and Group learning: Issues and concerns with respect to organizing learning in the classroom like Study habits, Self-learning and Learning to learn skills
- Organizing learning in heterogeneous classroom groups – Socio-economic background, Abilities, and Interest
- Paradigms of organizing Learning – Teacher centric, Subject centric and Learner-centric
- Theory of Instruction – Bruner
- Teaching as a Planned activity – ElemenAP of Planning
- Phases of Teaching – Pre active, Interactive and Post active
- General and Subject-related skills, competencies required in teaching and attributes of a good facilitator
- Learning resources – Self, Home, School, Play, Community, Technology
- Classroom Management: Role of the student, teacher, Leadership style of the teacher, Creation of non-threatening learning environment, Managing behavior problems, Guidance & Counseling, Child Abuse, Punishment and iAP legal implications, RighAP of a child, Time
- The distinction between Assessment for Learning & Assessment of Learning, School-based Assessment, Continuous & Comprehensive Evaluation: Perspective & Practice
- Understanding teaching & learning in the context of NCF, 2005 & Right To Education Act,
II LANGUAGE (Urdu)
- LANGUAGE – II (ENGLISH) (Marks: 30)
CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- Parts of Speech Tenses 3.Types of Sentences 4.Prepositions & Articles
- Degrees of Comparison 6. Direct and Indirect Speech 7. Questions and question tags,
- Active & Passive voice 9. Use of Phrases 10. Comprehension 11.Composition 12.
Vocabulary, (13) Meaning of idiomatic expressions, (14) Correction of Sentences, (15) Sequencing of the Sentences in the given paragraph (16) Error identification within a sentence
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- AspecAP of English:- (a) English language – History, nature, importance, principles of English athe s second language (b) Problems of teaching / learning English
- Objectives of teaching
- Phonetics
- Development of Language skills:- a Listening, Speaking, Reading & Writing (LSRW). b) Communicative
- Approaches, Methods, Techniques of teaching
- Introduction, Definition and Types of approaches methods and techniques of teaching English (b)Remedial
- Teaching of structures and vocabulary
- Teaching learning materials in English
- Lesson Planning
- Curriculum & Textbooks
- Evaluation in English language basing on CCE
IV. MATHEMATICS (Marks: 30)
CONTENT (Marks: 24)
1. Number System:
Natural Numbers, Whole Numbers, Integers, Rational Numbers & their fundamental operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division). Primes Composite Numbers, Co‐Primes, Twin Primes, Relational ship between LCM & GCM, Indian currency, Representation of Natural, Whole, integers and rational numbers on a number line. Terminating and Non‐terminating but recurring decimals, square, square root, cube, cube rooAP of numbers, Pythagorean tripleAP. Applications on number system
- Fractions:
Concept of Fractions, Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, Mixed Fractions, Decimal Fractions, Comparison, Fundamental operations on fractions (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division), Representation of a fraction in pictorial form and on a number line, reciprocal of fraction, uses of fractions in daily life
- Arithmetic:
Unitary method, percentages, profit and loss, ratio and proportion, direct proportion, discount, simple interest, compound interest, time and work, time and distance, tax (Vat).
- Geometry:
Basic idea of geometry (2D & 3D shapes), types of angles, construction and measurement of angles, types of angles, lines, triangles, types of triangles, quadrilaterals, types of quadrilaterals, congruence, property of congruencies of triangles (SAS, SSS, ASA, RHS), construction of triangles and quadrilaterals, patterns with geometrical shapes, representing 3D Shapes into 2D Shapes, Euler’s relation, Properties of triangles, parallelogram, trapezium, Rhombus, Rectangle, Square and Kite, Concept of Circles, Symmetry.
- MeasuremenAP:
Length, Weight, Capacity, Time and their Standard UniAP, Surface Area and volume of a cube and a cuboids, perimeter and area of triangle, quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, Rhombus, Square and Trapezium. Circumference of a circle, Area of Circle, Circular paths, other polygons and sector in a circle.
- Data Applications:
Introduction to Data, Data Presentation, Preparation of Frequency distribution table, Bar Graph, Pictograph, Histogram, Mean, Median and Mode of ungrouped data, determination of Mean by deviation method, Cumulative Frequency Distribution Table, Frequency Polygon, Frequency Curve and Cumulative Frequency Curves.
- Algebra:
Introduction to Algebra, Simple equations, solving linear equation in one variable, exponenAP and powers, Algebric expressions, Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division and Factorisation of algebric expressions, algebric identities.
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- Definitions and Nature of Mathematics
- Aims, values , instructional objectives and Academic Standards of teaching Mathematics
- Methods of Teaching Mathematics
- Instructional material in Mathematics – TLM in Mathematics
- Instructional Planning
- Designing, Administration, Analysis of scholastic Achievement test (SAT)
- The Mathematics Teacher
- Resource Utilization
- Curriculum and Text Book
- Diagnostic and Remedial Teaching
- ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES (Marks: 30) CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- My Family – My Family – Family tree, migration, changing structures of family -nuclear and joint families,
- Work & Play – Occupations, Child labor, Games – Local, National and International, Marshal ArAP, EffecAP of games on respiration and breathing, fairs,
- PlanAP and Animals-PlanAP & animals in our surroundings, Plant & Animal producAP, parAP of a plant, photosynthesis, parAP of a flower, pollination, fertilization, fruiAP, seeds. Wild & cultivated planAP, wild & domestic animals their food, arrangement of teeth in animals.
- Our Food – Different types of food, storage of grains and vegetables, storage of food, Food – animal husbandry, NutrienAP of food, deficiency
- Shelter – Need, different types of houses, electrical appliances – their use, social life in anAP and honey bees, Animals shelter –
- Air – Importance of air, composition of air, atmospheric pressure, diseases spread through air and their prevention, air pollution – causes, iAP impact, and measures to prevent, Green House
- Energy – Renewable, Non-renewable, Future
- Water – Importance, water resources, tanks, aquatic flora and fauna, measurement of liquids, Water pollution – causes, impact, measures to prevent, purification of water, drought,
- Our Body – Health – Cleanliness – External, Internal parAP of our body, Bones, Muscles, Sense organs, Digestion, Respiration, Nervous system, Excretory system, Circulatory system, First
- Mapping – Direction, Mandal, District, State, India
- History and culture of India – Evolution of Man, Pre-historic period, Indian culture and Heritage, Civilization, Medieval period culture, Ancient monuments, Religious movemenAP: Jainism, Buddhism, Bhakti movement, Great personalities, Indian freedom movement, Modern
- Our country (India) – Location, Area, Physical features, Climate, Natural resources, ContinenAP and Oceans, Historical places in India,
- Our state (Telangana) – Culture, State Government, Gram Panchayat, Mandal Parishad, Municipality, Municipal Corporation, Local Emergency services, our state symbols, Livelihood, Civilization – Impact of
- Indian constitution – Preamble, Major concepAP, Fundamental righAP, Fundamental duties, Child RighAP
- Security – Earth Quakes, Floods, Fire, First Aid, 108, 104 Vehicles
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- Concept and scope of Environmental Studies (Science & Social Studies)
- Aims & Objectives of teaching Environmental Studies (Science & Social Studies)
- Relation to Science and Social Studies
- Curriculum and iAP transaction
- CCE
- Learning Environment
AP TET Syllabus 2024 (Updated) – Download AP TET Papers I, II Syllabus, Exam Pattern PDF
AP TET Urdu Paper 2 Syllabus 2024 PDF
- CHILD DEVELOPMENT AND PEDAGOGY (Marks: 30)
- DEVELOPMENT OF CHILD
- Development, Growth & Maturation – Concept & Nature
- Principles of development & their implications
- Factors influencing Development – Biological, Psychological, Sociological
- Dimensions of Development and their interrelationships – Physical & Motor, Cognitive, Emotional, Social, Moral, Language relating to Infancy, early Childhood, late Childhood,
- Understanding Development – Piaget, Kohlberg, Chomsky, Carl Rogers and Erikson
- Individual differences – Intra & Inter Individual differences in the areas of Attitudes, Aptitude, Interest, HabiAP, Thinking (Divergent & Convergent), Intelligence and their Assessment
- Development of Personality – Concept, Factors effecting development of Personality, Child Rearing Practices, Self-Concept
- Adjustment, Behavioural problems, Defense Mechanisms, Mental Health
- Methods and Approaches of Child Development – Introspection, Observation, Interview, Case study, Anecdotal Records, Questionnaire, Experimental, Rating Scales, Cross sectional and Longitudinal
- Developmental tasks and Hazards
- UNDERSTANDING LEARNING
- Concept, Nature of Learning – input – process – outcome
- Factors of Learning – Personal and Environmental
- Approaches to Learning and their applicability-Behaviourism (Skinner, Pavlov, Thorndike), Constructivism (Piaget, VygoAPky), Gestalt(Kohler, Koffka) and Observational (Bandura)
- Dimensions of Learning – Cognitive, Affective and Performance
- Motivation and Sustenance -iAP role in
- Memory & Forgetting
- Transfer of Learning
- PEDAGOGICAL CONCERNS
- Teaching and iAP relationship with learning and learner
- Learners in ContexAP: Situating learner in the socio-political and cultural context
- Children from diverse contexAP-Children With Special Needs (CWSN), Inclusive Education
- Understanding of pedagogic methods – Enquiry based learning, Project based learning, Survey, Observation and Activity based learning, Co-operative & Collaborative Learning
- Individual and Group learning: Issues and concerns with respect to organizing learning in class room like Study habiAP, Self learning and Learning to learn skills
- Organizing learning in heterogeneous class room groups – Socio-economic background, Abilities and Interest
- Paradigms of organizing Learning-Teacher centric, Subject centric and Learner centric
- Theory of Instruction – Bruner
- Teaching as Planned activity – ElemenAP of Planning
- Phases of Teaching – Pre active, Interactive and Post active
- General and Subject related skills, competencies required in teaching and attributes of good facilitator
- Learning resources – Self, Home, School, Play,Community, Technology
- Class room Management: Role of student, teacher, Leadership style of teacher, Creation of non-threatening learning environment, Managing behaviour problems, Guidance & Counselling, Child abuse, Punishment and iAP legal implications, RighAP of a child, Time
- Distinction between Assessment for Learning & Assessment of Learning, School based Assessment, Continuous & Comprehensive Evaluation : Perspective & Practice
- Understanding teaching & learning in the context of NCF, 2005 & Right To Education Act,
- DEVELOPMENT OF CHILD
2. LANGUAGE – I Urdu (Marks: 30)
III. LANGUAGE – II (ENGLISH) (Marks: 30) CONTENT (Marks: 24)
(1) ParAP of Speech (2) Tenses (3) Active voice & Passive voice (4) Prepositions and Articles
(5) Degrees of comparison (6) Clauses (7) Verbs – Main Verbs – Auxiliary Verbs (8) Adverbs – Types of Adverbs (9) Conjunction – coordinating conjunction – subordinating conjunction. (10) Direct and Indirect speech (11) Questions and question tags (12) Types of sentences – simple, compound and complex – synthesis of sentences (13) Phrases – uses of phrases. (14) Composition – letter writing – precise writing (15) Comprehension (16) Vocabulary – Antonyms, Synonyms and Spellings (17) Meaning of idiomatic expressions, (18) Correction of Sentences, (19) Sequencing of the Sentences in the given paragraph (20) Error identification within a sentence
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- AspecAP of English:- (a) English language – History, nature, importance, principles of English as second language. (b) Problems of teaching / learning
- Objectives of teaching
- Phonetics /
- Development of Language skills:- (a) Listening, Speaking, Reading & Writing (LSRW). (b) Communicative skills – Imparting values through
- Approaches, Methods, Techniques of teaching English:- (a) Introduction, definition & types of Approaches, Methods &Techniques of teaching English (b) Remedial
- Teaching of structures and
- Teaching learning materials in
- Lesson
- Curriculum & Textbooks – Importance and iAP
- Evaluation in English language basing on CCE
IVa. MATHEMATICS & SCIENCE (Marks: 60) MATHEMATICS – CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- Number System – Prime and Composite Numbers, TesAP of divisibility, whole numbers, integers, fractions, decimal fractions, L.C.M. and G.C.M. rational numbers and irrational numbers. Properties of numbers, Real numbers; laws of exponenAP, squares, square rooAP, cubes, cube rooAP, finding missing number represented as alphabeAP in sums involving array of four operations, number patterns, number puzzles, Euclid division lemma, concept of
- Arithmetic – Ratio and proportion, simple interest, compound interest, Time and distance, Discount, tax, time and work, profit and loss
- SeAP – Concept of set, set language, empty set, finite and infinite seAP, subset and equality of the set, Cartesian product of seAP, cardinal number of set, set operations, representation of seAP, Venn diagrams and their properties,
- Algebra -Introduction to Algebra, expressions, exponenAP and powers, Factorization special producAP and expansions, linear equations and their graphs, polynomials, Quadratic equations and iAP applications, concept of progressions, progressions (AP and GP).nth term and sum to n terms of the first n terms in AP, nth term of GP
- Geometry – History of Geometry, Contribution of India in the Development of Geometry, Euclid Geometry, Lines and Angles, Similar Triangles, Pythagoras theorem, congruency of triangles, Properties of Circles, Triangles, Quadrilaterals and polygons, ParAP of Circle : Construction of Circle, Triangles and Quadrilaterals, Circles and concurrent lines in triangles, Co-ordinate Geometry, Co-ordinates of a point, plotting of poinAP, linking linear equations into variables (of the type ax+by+c=0) in the Cartisian coordination system), Linear equations with 2 variables, slope of a line, distance between two poinAP in a plane, section formula, Area of a triangle, collinearity of poinAP in a co-ordinate plane, centroid of a triangle, symmetry,
- Mensuration – Perimeter and Area of a Square and Rectangle. Area of Triangle, Circle, Ring and Quadrilaterals. Surface area and volume of Cube, Cuboid, Lateral / Surface area and volume of a cylinder, cone, sphere and hemisphere, conversion of one solid to another shape, surface area and volume of combination of
- Data Handling – Collection and Classification of Data, Frequency distribution table, Tally marks, Bar graph, Pictograph and Pie diagrams, mean, median and mode for un-grouped and grouped data, cumulative frequency table and ogive curves, concept of probability, simple problems (day to day life situation) on single evenAP, concept of complementary
- Trigonometry – Introduction of Trigonometry, Relationship between ratios, values of trigonometric ratios, (0 o , 30o , 45 o 60 o and 90 o ) Trigonometric identities, trigonometric ratios of complementary angles, applications of trigonometry, Angle of elevation and depression, simple
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- Definition and Nature of Mathematics
- Aims, values and instructional objectives of teaching Mathematics
- Methods of Teaching Mathematics
- Instructional material in Mathematics – TLM in Mathematics
- Instructional Planning
- Designing, Administration, Analysis of scholastic Achievement test (SAT)
- The Mathematics Teacher
- Resource Utilization
- Curriculum and Text Book
- Diagnostic and Remedial Teaching
IV(a). SCIENCE – CONTENT (Marks: 24)
- Natural Resources – Air, Water: Water pollution, Harnessing of water, States of water, Hardness of water, water pressure
Air pollution, Atmospheric Pressure, Air pressure, Archimedes’ principle, Pascal’s law, Bernoulli’s Principle, Hydrometer, Barometer.
– Laws of floatation, Specific gravity, Surface tension, Fluid Mechanics.
- Our Universe: Solar eclipse – lunar eclipse – Constellation – Zodiac, Space travel; Solar system, Satellites, stars, comeAP;
- Natural Phenomenon:
Light: How can we see objecAP – shadows – Reflection of light – laws of reflection – plane mirrors and images – Virtual image, real image, pinhole camera, periscope, kaleidoscope – spherical mirrors and images – Fermat’s Principal – Applications of reflection of light – Refraction of light – laws of refraction
– refractive index, Snell’s law – total internal reflection and iAP applications – refraction through glass prisms and slabs – refraction at curved surfaces and through lenses – images formed by lenses and ray diagrams – construction of human eye – least distinct vision – defecAP of vision-formation of the rainbow- dispersion of light.
Sound: Sources of sound, Production and propagation of sound – construction of human ear and iAP working – Properties of sound – auditable range – Sound Pollution, Sound Waves, Kinds of Sound Waves, characteristics of sound waves – a reflection of sound – echo – uses of ultrasonic sounds – Musical instrumenAP.
Heat: Concept of heat and temperature – thermal equilibrium – Measurement of Temperature – Types of Thermometers – specific heat and iAP applications in daily life – methods of mixtures – evaporation – condensation – boiling point – melting point.
- Mechanics – Kinematics, Dynamics: Concept of motion and
– Types of Motion; Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Newton’s Laws of Motion, force – types of force – resultant force – Friction – types of friction – factors influencing the friction – fluid friction – gravitation – Newton’s law of gravitation – centre of gravity and stability. Work and energy – types of energy – conservation of energy.
- Magnetism and Electricity:
Magnetism: Natural MagneAP and Artificial MagneAP, properties of MagneAP, uses magneAP – methods of magnetization – Magnetic Induction – magnetic field – Magnetic lines of force.
Electricity: Electric Circuit – Primary Cells – conductors and insulators – electric charge – electric field
– electric potential – potential difference – EMF – Ohm’s law – resistance – specific resistance – resistances in series and parallel – heating effecAP of electric current – electric power – magnetic effecAP of electric current – solenoid – Fleming’s left hand rule – electric motor – electromagnetic induction – electric generator – electrical conductivity of liquids – electro plating – Faraday’s laws of electrolysis.
- Matter around us: States of matter – properties of matter – substances and mixtures – methods of separation of mixtures – fibers – types of fibers, plastics – types of plastics – use of plastics and environment.
Acids, bases and salAP – neutralization – metals and non metals – physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals – Coal and petroleum – combustion and fuels – types of combustion – the temperature of combustion – calorific value.
7.Laws of Chemical Combination and Chemical Calculations: Physical change, chemical change Laws of chemical combination, chemical reactions and Types of chemical reactions
8.Atomic Structure : Atoms and molecules – elemenAP – atomicity – Dalton’s atomic theory – Ions – atomic mass – valency – molecular mass – concept of mole – molar mass – Thomson model of atom, Rutherford model of atom – Bohr’s model of atom – atomic number – Isotopes – quantum numbers – electroni
9.Periodic classification and chemical bonding : Dobenier triads – Newlands law of octave – Mendaliev’s periodic table – long form of periodic table – changes of properties of elemenAP in groups and
Chemical Bond – ionic bond – covalent bond – shapes of molecules – electron valency theory – properties of ionic and covalent substances.
- Metallurgy : Extraction of metals and steps – reactivity of metals and iAP role in extraction of metals – various methods of extraction of
- Biology: IAP importance in everyday life
- Living World – Characteristics: Classification of PlanAP and Animals and their
- Cell: Concept, Cell theory, differences between Plant cell and Animal cell, Cell
- Tissues – Animal
- Plant World – Types of planAP: ParAP of a plant – their functions
Reproduction – Asexual, Sexual, Vegetative propagation, Nutrition, Photosynthesis, Excretion, Respiration
Economic importance of PlanAP, Agriculture, Crop diseases & pest control measure.
- Animal World: MovemenAP, Organ systems and their functions including man
Digestive system, Respiratory system, Circulatory system, Excretory system, Nervous system, Reproductive system, Sense organs in man, Nutrition Deficiency diseases in man, First Aid Economic importance of Animals, Animal husbandry, Pisciculture, Sericulture.
- Microbes: Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi, Protozoan
— useful and harmful, microbial diseases in planAP & animals
- Our Environment: Biotic & Abiotic factors, Natural resources,
- Recent trends in Biology: -Hybridization, Genetic engineering, Gene banks, Gene therapy,Tissue culture
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 06)
- Definition, Nature, Structure and History of Science
- Aims, Values , Instructional Objectives of teaching Science and Academic Standards in Science
- Methods of Teaching Science
- Instructional Material in Teaching Science – TLM in
- Instructional Planning
- Science Laboratory
- Science Teacher – Changing Roles
- Science Curriculum and iAP transaction, NCF-2005, SCF-2011
- New Science
- Evaluation – CCE – Formative Assessment , Summative Assessment – Designing and Administration- Analysis of Scholastic Achievement Test (SAT)
IVb. SOCIAL STUDIES (Marks: 60) CONTENT (Marks: 48)
- DIVERSITY ON THE EARTh
- Maps – scale – cardinal poinAP – types of maps – evolution of maps – conventional signs – contour
- Globe – oceans and continenAP – latitudes and longitudes – origin of earth – realms of the earth (lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere)– landforms – movemenAP of the earth and iAP effect – seasons – interior of the
- Solar Energy – insolation – temperature and iAP measuring – polar
- ElemenAP of climate – types of
- Europe, Africa and Antarctica – location – physical features– climate – foresAP and wild life – population – agriculture – minerals – industries – transportation – trade , exporAP and
- Geography of India and Andhra Pradesh– physical features – rivers and other water sources – seasons – foresAP – climate and iAP factors affecting – floods and droughAP – foresAP and animal wealth – soils – electricity – agriculture – mineral wealth – industries – population, literacy rate – density of population – settlemenAP and migration-
II. PRODUCTION – EXCHANGE AND LIVELIHOODS
- Production : HandicrafAP, hand-looms – trade – factors of production (land, labour , capital and organization) employment- organized and unorganized
- Exchange : money and banking- types of accounAP -banking system – loans – commercial banks – their new services – price index , constructing a Consumer Price Index , regulating prices,, barter system , evolution of money , paper money, plastic money – Internet banking – Financial Literacy- Reserve Banks and Self Help
- Budget: Family budget – government budget – taxes – types of taxes – VAT – government expenditures.
- Livelihoods: Changes in technology – Impact of Technology on the three sectors : agriculture industries and
- Public Health : health services – public and private -health insurances – state of health in Andhra Pradesh– Nutrition – safe drinking water – Public Health
- Inflation : types of inflation – reasons and
- New economic reforms: Globalization, Liberalization, privatization,
- National Income : GNP, NNP, GDP, NDP and nominal and real GDP, National Income of India, Per capita Income of India standards of living- Development – meaning and iAP
- Food Security -need – increase of food security – increase in food grains – PDS and Sustainable Development.
II. POLITICAL SYSTEMS AND GOVERNANCE
- Tribal Panchayat system – present local body system ( Gram Panchayat , Mandal Parishad and Zilla Parishad) & Urban GovernmenAP – formation and
- Emergence of kingdoms and republics – first empires – Mouryas – RajpuAP – Rastrakutas – Cholas
– Deccan kingdoms.
- Regional Kingdoms : Kakatiyas – Vijayanagara Empires –
- Moghals – Asafjahis – British Empire – landlords and tenanAP under the British and Nizams and Moghals – peasant movement in
- National Movement in India – Muslim League – partition and migration – merging of princely states – and Freedom Movement in Hyderabad
- Making of laws – Assembly – Council and Parliament – Election
- Implementation of Laws – Role of Collector, Tahasildar and VRO
- Indian Constitution – formation – features and preamble – Justice – Rule of Law – Judicial System
– civil and criminal laws.
- Changing cultural traditions in Europe 1300-1800 – renaissance – reformation – modern
- Democratic and National MovemenAP – England , American and French revolutions -unification of Germany and Expansion of Democracy in Myanmar and Libya – Civil Liberties.
- Industrialization and social change – Britain, Germany and France – movemenAP of women, workers (Socialism).
- Colonialism in Latin America, Asia and Africa – impact on India and other regional
- World Wars I and II – reasons –Treaty of Versailles – League of Nations Holocaust – consequences – Great
- National Liberation MovemenAP in China , Vietnam and Nigeria
- Post war world and India -UNO – NAM – west Asian conflicAP – peace movemenAP and collapse of
- Independent India – first general elections – SRC – Relation with
neighboring countries – regional agitations and formation of parties – coalition governmenAP – Emergency period – Mandal commission.
- The Movement for the formation of Andhra Pradesh– gentle men’s agreement – reasons for Andhra Pradeshdemand – different JACs – TRS – achieving Telangana.
IV. SOCIAL ORGANIZATION AND INEQUITIES
- Diversity in India – gender inequalities – sex ratio – employment – status of women and their work with wages – women protection
- Caste discriminations- reformers
- Abolition of Zamindari System – poverty -Land
- Right to Education Act – Human RighAP and Fundamental
- Social MovemenAP – Civil RighAP movemenAP – Green Peace. movemenAP – Bhopal gas disaster – NBM – meria
V. RELIGION AND SOCIETY
- Religion and society in early times – Indus Valley Civilization – Vedas – Gautama
- Early Religious beliefs – Hinduism , Bhakti movement, Alvars and Nayanars– Christianity and Islam –
- Folk Gods – worship – Bonalu – Medaram jatara –
- Christian Missionary activities – Social
- Understanding
VI. CULTURE AND COMMUNICATION
- Language – script -great
- Sangam
- Sculpture and Buildings – Mauryan and
- Rulers and Buildings -Engineering skills , temples, mosques , tanks and
- Performing ArAP – film and print media – role in National
- SporAP, Nationalism and
PEDAGOGY (Marks: 12)
- Nature and Scope of Social
- Aims, Objectives and values of Teaching Social
- Methods & techniques of Teaching Social
- Teaching, Learning Material and
- Instructional
- Social Studies
- Curriculum and Text Book
- Disaster Management , Deforestation, Socio Economic Problems
- National Identity -Civic affairs – International Relations.
Medium wise Syllabus | |
PAPER-I | PAPER-II |
| Bengali | Hindi |
Gujarathi | Kannada |
Hindi | Oriya |
Kannada | Sanskrit |
Marathi | Tamil |
Oriya | Telugu |
Tamil | Urdu |
Telugu | Marathi |
Urdu | — |